Varicose Veins in Korea
Varicose Veins — How to Achieve Smooth, Healthy Legs
Varicose Veins: How Do They differ from other conditions?
Although similar, leg veins, chronic venous insufficiency, and varicose veins are separate and distinct terms that refer to different things:
Leg veins is not a condition but an anatomical term referring to the veins located in the legs. These veins are responsible for carrying blood back to the heart from the lower limbs.
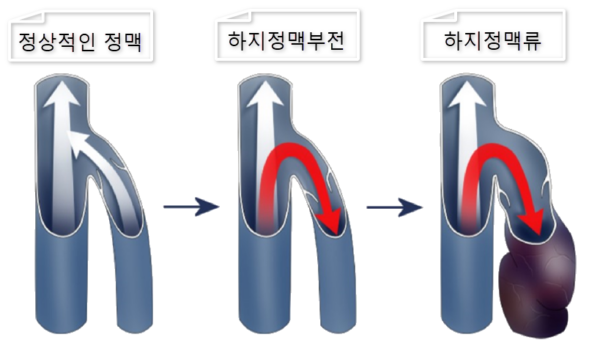
Chronic Venous Insufficiency, however, is a medical condition and functional disorder of the leg veins, where blood does not flow properly toward the heart and instead pools in the legs. Unlike varicose veins, there may not be any visible bulging, but the veins are not working effectively.
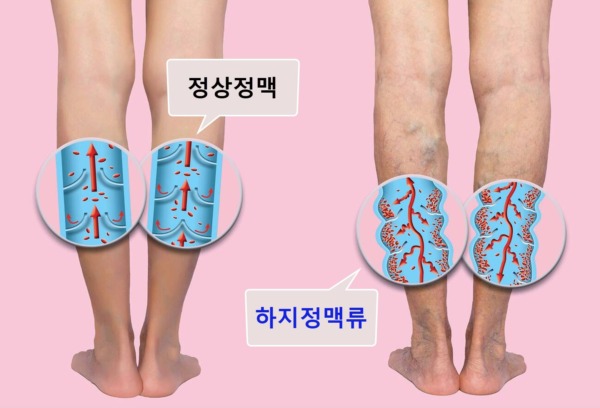
Varicose Veins are visually recognizable by twisted, bulging veins that appear on the surface of the skin. It is a condition that occurs due to malfunctioning valves in the veins, leading to backward or stagnant blood flow, causing the veins to swell and visibly protrude.
Causes of varicose veins
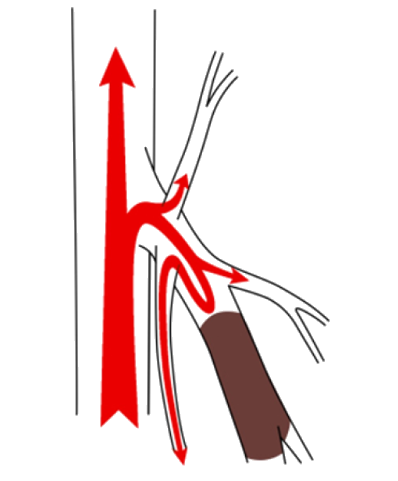
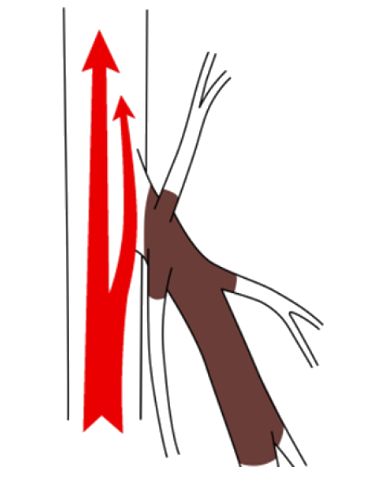
Inside the veins are small valves, like tiny doors, that prevent blood from flowing backward. These valves are crucial for stopping venous blood from flowing downward due to gravity.
When these valves malfunction, blood that should be moving upward flows backward toward the ankles. As blood pools and becomes stagnant, the veins stretch and varicose veins (chronic venous insufficiency with visible bulging) can develop.
Varicose veins occur due to damage to these venous valves, and the main causes include:
Diagnosis and treatment of varicose veins
Varicose veins are often visibly diagnosable, but for an accurate diagnosis and to develop an effective treatment plan, a vascular ultrasound exam is essential.
▪️ Vascular Ultrasound Examination
This test confirms the presence and location of blood reflux caused by valve dysfunction.
Using B-mode imaging, anatomical issues are identified, while Doppler ultrasound evaluates the direction, speed, and volume of blood flow.
Diagnostic Criteria for Venous Reflux:
- Deep veins: Reflux lasting more than 1.0 second
- Superficial veins: Reflux lasting more than 0.5 seconds
- Perforator veins: Reflux lasting more than 0.35 seconds
▪️ Treatment Options for Varicose Veins
The appropriate treatment is chosen based on the patient’s condition, the size and location of the varicose veins, and their overall health.
▪️Early-stage, small varicose veins:
Sclerotherapy or laser treatment can be effective.
▪️Moderate-sized varicose veins:
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) or laser treatment is typically effective.
▪️Large, complex varicose veins:
Microphlebectomy (surgical removal of varicose veins through tiny incisions) may be necessary.
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) for Varicose Veins is a treatment method where a radiofrequency catheter is inserted into the vein, and heat is used to seal and close the affected vein from the inside.
Compared to laser treatment, RFA typically causes less pain, offers faster recovery, and allows patients to return to daily activities within 1–2 days after the procedure.
Sclerotherapy for Varicose Veins is a treatment in which a sclerosing agent (a special medication) is injected into the affected vein to harden the vessel and block blood flow.
The procedure is preceded by a vascular ultrasound examination to check for abnormalities in the saphenous and perforator veins.
The number of treatment sessions may vary depending on the individual’s condition.
Microphlebectomy, a procedure commonly performed in the past, involves the direct removal of veins with venous reflux.
This surgery is sometimes performed alongside other varicose vein treatments. However, since it leaves small scars about 2 mm in size, patients are usually monitored for around 6 months after the procedure. If residual branch veins remain, additional treatments may be performed.
Varicose Vein Symptoms
Varicose Veins Complications
Post-Operative Precautions
SH Clinic’s Know-How & Proof of Results
The treatment for varicose veins at SH Clinic is a complete closure surgery that does not leave behind the root vein. We have the know-how to fundamentally prevent the possibility of recurrence.
| Conventional Closed surgery | SH Clinic’s Complete Closure Surgery | |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Leaves about 5mm of the proximal stump of the great saphenous vein | Completely closes the proximal stump of the great saphenous vein, leaving no stump |
| Blood Flow Stability | The stump cannot withstand pressure, causing new reflux pathways to form | Pressure is stably dispersed, creating a comfortable and stable blood flow path |
| Recurrence Risk | There is a possibility of recurrence | Low risk of recurrence |
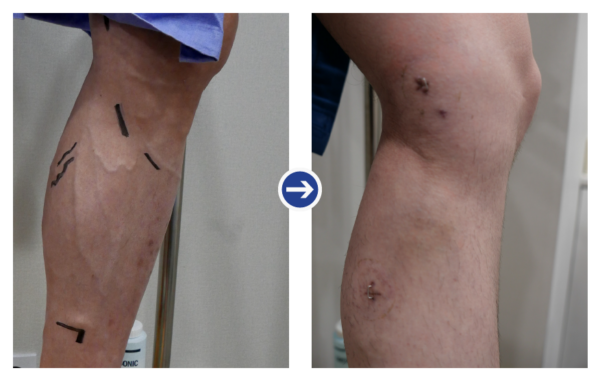 Before and after photos of high frequency treatment 1
Before and after photos of high frequency treatment 1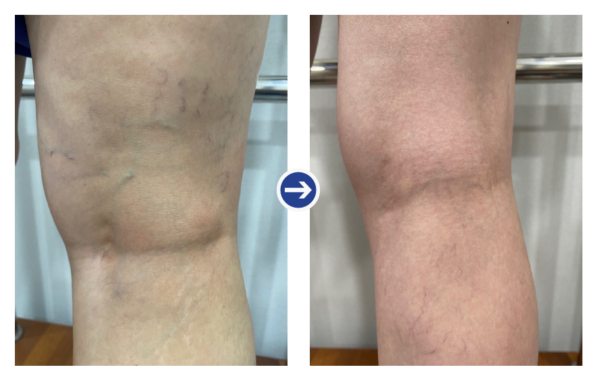 Before and after photos of high frequency treatment 2
Before and after photos of high frequency treatment 2
Treating Varicose Veins for Comfort and Confidence
Common Diagnoses for Patients with Venous Pain
The diagnosis of chronic venous insufficiency is made through ultrasound examination. Ultrasound allows observation of blood flow within the veins, assessment of valve function, and evaluation of vein dilation to accurately detect reflux.
symptoms of venous insufficiency
Treatment Methods for Chronic Venous Insufficiency
Treatment for chronic venous insufficiency varies depending on the severity of symptoms, and several methods of treatment are available. It is important to consult with a specialized medical professional to select the appropriate treatment.
In the early stages, non-surgical treatments are often effective, but if symptoms worsen, surgical treatment may be necessary.
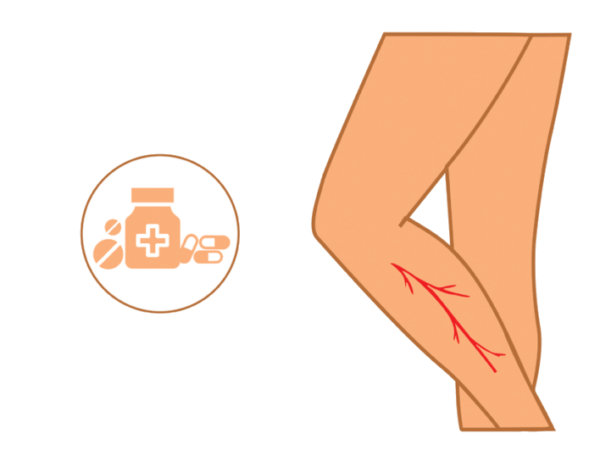
There are medicines that can help relieve symptoms by increasing vascular tone, thereby reducing reflux volume and slowing the progression of venous insufficiency. However, since medication alone cannot provide a complete cure, it is important to consult with a specialized medical professional to determine the best treatment plan.
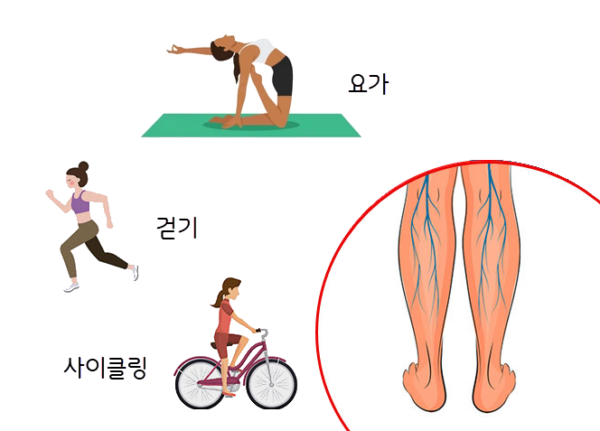
Exercise therapy is very important for improving blood circulation and alleviating symptoms. Activities such as walking, cycling, ankle exercises, and yoga can be helpful. It is important to consult with a doctor before starting exercise and to choose the appropriate exercise methods.
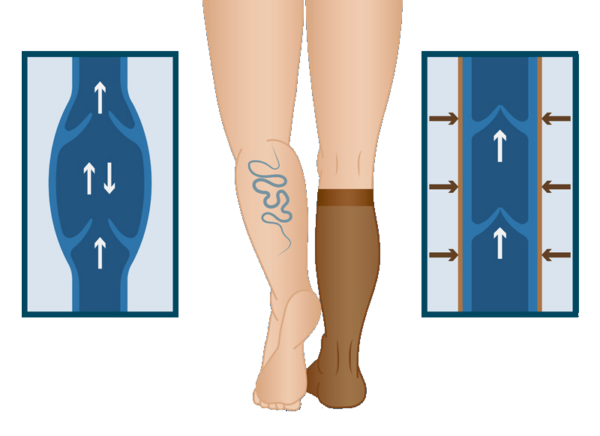
Compression stockings help distribute pressure evenly along the leg veins, promoting smooth blood flow back toward the heart and alleviating symptoms.
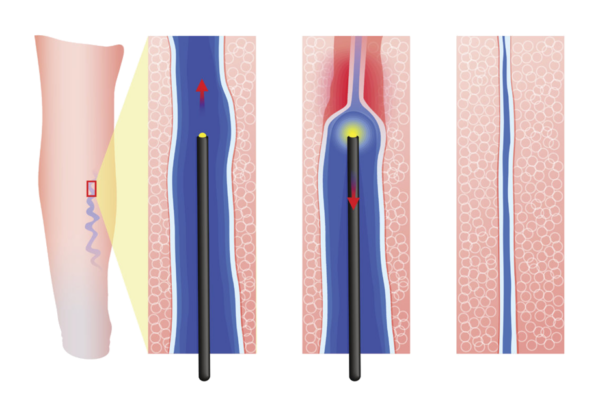
Laser therapy is a relatively new non-surgical treatment method that uses high heat, with a peak temperature of up to 1,000°C, to close off the affected veins. Once closed, these veins no longer carry blood, which is then redirected through other healthy veins. Over time, the closed veins are naturally absorbed by the body.
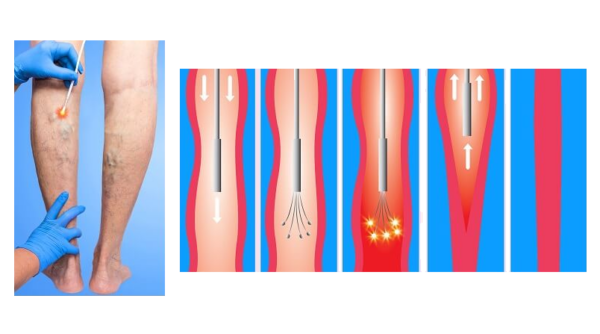
HIFU (High Intensity Focused Ultrasound) therapy is a minimally invasive treatment method increasingly used alongside laser therapy. It delivers relatively lower heat, about 120°C, to the walls of the diseased veins, causing them to contract and close. The closed veins are gradually absorbed by the body over time, and blood flow is redirected through other healthy veins.
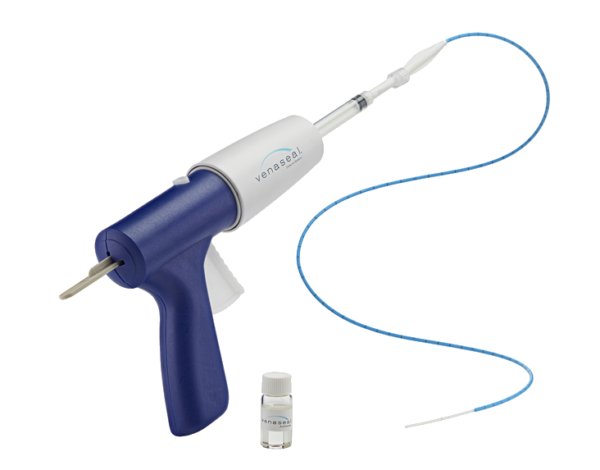
This method involves injecting a medical adhesive called Venaseal into the affected vein to close it. Over time, the vein is naturally absorbed by the body.
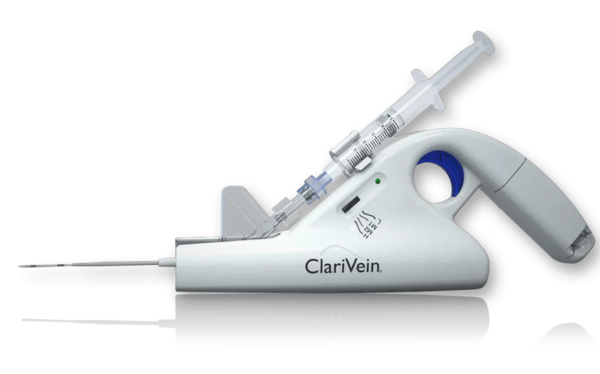
ClariVein is a procedure that combines mechanical damage to the vein’s inner lining with sclerotherapy to close the diseased vein and restore normal blood flow. It offers advantages such as a quick recovery time, less pain, and no scarring.
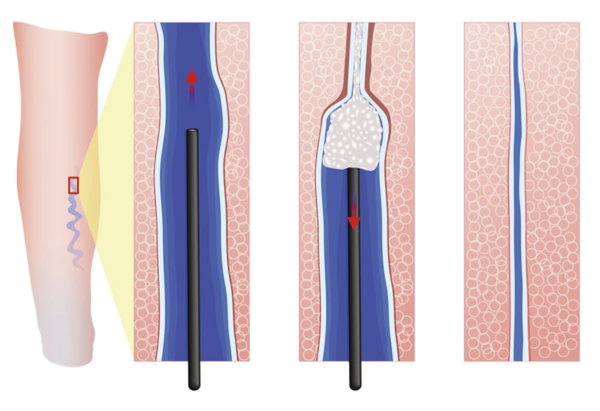
Sclerotherapy involves injecting a medication into the vein that irritates the vein walls, causing them to stick together and blocking blood flow through the vein. The closed vein is then gradually absorbed by the body and disappears over time. This treatment is suitable for small varicose veins and spider veins.
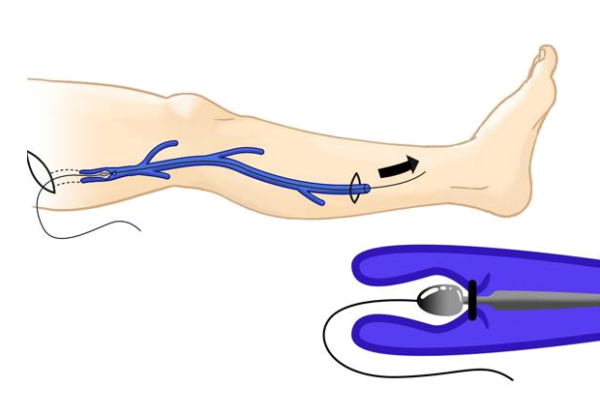
Vein Stripping is a procedure used to treat severe varicose veins. It is a method that minimizes incisions and physically removes the affected veins. A tool called a stripper is inserted to extract the enlarged or abnormal veins, thereby restoring normal blood flow.
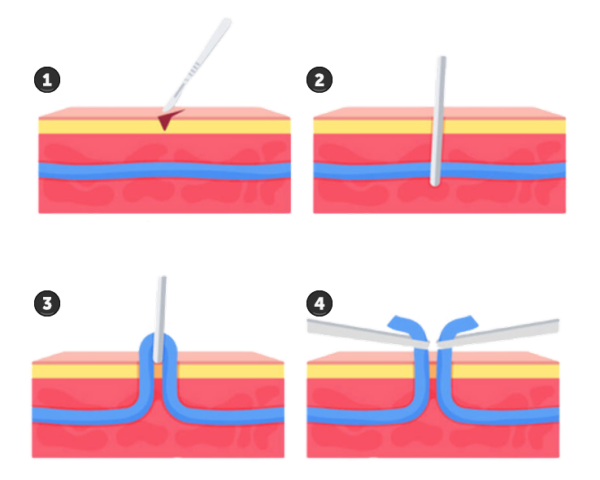
Local excision surgery involves making a minor incision to remove visibly protruding varicose veins or small, localized veins. Over time, blood flow normalizes, and patients experience improvement in symptoms such as swelling, pain, and fatigue.