Ovarian Cancer Screening in Korea
Ovarian cancer comes silently. Regular screening is the best prevention.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is a cancer that occurs in the ovaries, which are located on both sides of the uterus and produce follicles and female hormones. It has a relatively low incidence rate, with about 1,000 to 1,200 cases per year, but it is a fatal cancer with the highest mortality rate among female cancers. However, if the cancer is detected early and surgery is performed while it is limited to the ovaries and has not spread, the cure rate is 90%.
The best way to prevent ovarian cancer is to increase the probability of early detection through regular ultrasound examinations and blood tests.
Causes of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is a cancer that is mostly found in middle-aged women in their 40s and older. Although the incidence rate is low, there are almost no early symptoms, so it is only discovered in stages 3 and 4, and so regular checkups are necessary.
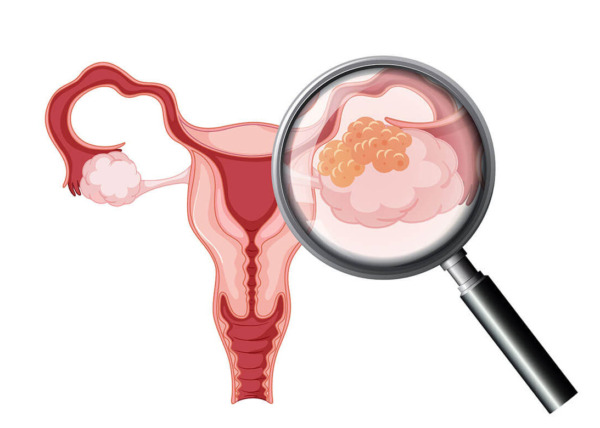
Diagnosis of ovarian cysts
Ovarian cysts usually appear as fluid-filled sacs, so examination should be undertaken carefully.
SH Clinic increases the accuracy of examinations through precise imaging diagnosis.

Medical Interview 
Ultrasound examination 
Blood test 
MRI scan
SH Clinic Examination System – The latest 4D precision ultrasound examination
Women in their 20s or older who are sexually active should have a gynecological checkup at least once a year.
Recommended Tests Based On symptoms
|
Symptoms |
Inspection items |
|---|---|
|
▫️ Increased vaginal discharge, odor, and itchiness |
▪️ Basic gynecological examination |
|
▫️ Bleeding during sexual intercourse |
▪️ Cervical cancer screening, cervical colposcopy, human papillomavirus screening, ultrasound, STD screening |
|
▫️ Irregular menstruation, irregular bleeding, excessive menstrual bleeding, decreased menstrual flow |
▪️ Ultrasound examination, hormone examination, cervical cancer examination, ovarian function examination |
|
▫️ Pain during intercourse, pain during ovulation, severe menstrual pain, or lower abdominal pain |
▪️ Internal examination, ultrasound examination, gender examination, simple cold examination, urine examination |
|
▫️ Warts or bumps around the vaginal opening or anus |
▪️ STD test, cervical cancer test, cervical colposcopy, iodine staining test |
|
▫️ If you want to maintain vibrant health after middle age |
▪️ Women’s cancer screening, women’s comprehensive screening, menopause screening |
|
▫️ If you want to simply check for adult diseases and cancer, etc. |
▪️ Molecular Genetic Cancer Screening (Blood Test/Accuracy 99%) |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer is a malignancy that occurs in the ovaries, which are responsible for producing eggs and female hormones. Despite its relatively low incidence, it has the highest mortality rate among female cancers. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve survival rates.
What are the common symptoms of ovarian cancer?
Common symptoms include vaginal bleeding, pain during intercourse, abdominal distension, unexplained pelvic pain, indigestion, constipation, and fluctuations in weight. These symptoms can be subtle, making regular screenings important for early detection.
Who is at risk for developing ovarian cancer?
Risk factors include a family history of breast, colon, or ovarian cancer; personal history of breast cancer; early onset of menstruation (before age 12); never having been pregnant or given birth; and having the first child after age 30.
How is ovarian cancer diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of medical history review, ultrasound examinations, blood tests, and MRI scans. Precise imaging techniques are used to increase the accuracy of the examination.
What screening methods are recommended for ovarian cancer?
Regular ultrasound examinations and blood tests are recommended to increase the probability of early detection. Women over the age of 20 who are sexually active should have a gynecological check-up at least once a year.
What is the cure rate for early-detected ovarian cancer?
If ovarian cancer is detected early and surgery is performed while it is limited to the ovaries and has not spread, the cure rate is approximately 90%.
