Uterine Fibroid Removal in Korea
Non-incision ultrasound treatment for uterine fibroids
Uterine Fibroid Removal: Treating the most common Female tumor
Uterine fibroids are benign tumors that develop in the smooth muscles that make up the majority of the uterus, and are particularly common in women in their 30s and 40s.
The exact cause of uterine fibroids is not yet known, but female hormones (estrogen) and genetic factors may play a role.
Although uterine fibroids are not cancerous, they can cause various symptoms depending on their size, number, and location. Early detection and accurate diagnosis is important in order to receive appropriate treatment.
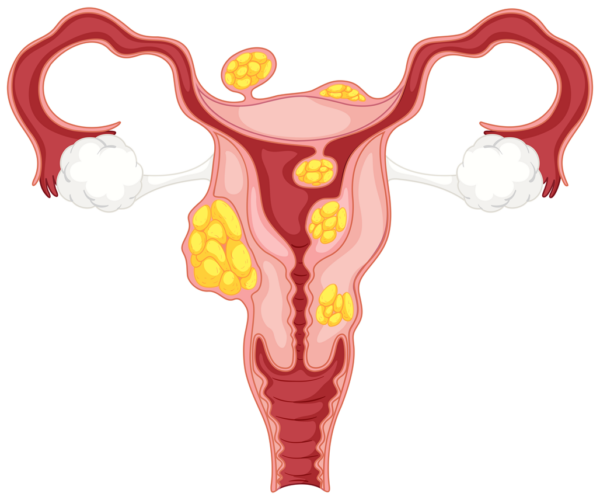
Symptoms of uterine fibroids
About 10-20% of uterine fibroids cause the following symptoms depending on their size, number, and location.
If they interfere with daily life or grow larger, treatment is essential.
Increased pelvic pain
This occurs as the size of the uterus increases in proportion to the size of the tumor.
Pressure
This occurs when enlarged uterine fibroids put pressure on the organs surrounding the uterus.
Infertility and miscarriage
Depending on the size and location of the fibroid, it may interfere with safe embryonic implantation.
Increased menstrual bleeding
Menstrual cramps and bleeding irregularity can become more severe.
Types of Uterine Fibroids
Depending on where they occur in the uterus, uterine fibroids are divided into intramural, subserosal, and submucosal fibroids categories. Their size gradually increases due to female hormones and growth hormones.
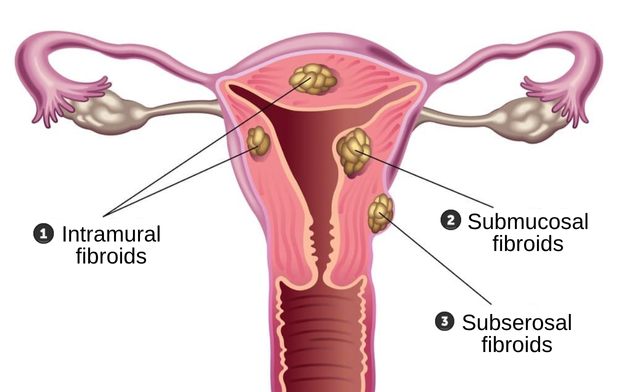
1. Intramuscular fibroids
These fibroids develop in the uterine muscle layer, changing the shape of the uterus, and increasing the area of the endometrium, causing severe menstrual pain and increasing the amount of menstrual blood.
2. Submucosal fibroids
This is the most dangerous type of fibroid, occurring in the endometrium. Regardless of the size, there is a high risk of bleeding and other complications, and they can be a direct cause of infertility.
3. Subscapular fibroids
These fibroids develop within the membrane surrounding the uterus and usually cause no noticeable symptoms. The fibroids can also elongate, forming a stalk.
Is uterine fibroid removal really necessary?
Uterine Fibroid Removal: Methods
Treatment for uterine fibroids may vary depending on the size, location, and symptoms of the fibroids, as well as the patient’s age and health.
Importance of Treating uterine fibroids before pregnancy
Treatment of uterine fibroids is recommended to ensure a healthy pregnancy. The endometrium is the part of the uterus where the embryo is implanted. If there are uterine fibroids in the endometrium, it can interfere with implantation, possibly causing miscarriage. Treatment of uterine fibroids is personalized based on the size and growth rate of the individual’s uterine fibroids.
Early pregnancy
Depending on the location and size of the uterine fibroids, the risk of infertility or miscarriage may increase, making it difficult to become pregnant.
Second trimester
During pregnancy, uterine fibroids may degenerate, causing pain and a risk of early miscarriage.
Late pregnancy
The weight of uterine fibroids can cause uterine atony (muscle weakness), which may increase the risk of dystocia (difficult birth) and postpartum bleeding.
Treatment of uterine fibroids and adenomyosis
Most cases of uterine fibroids and adenomyosis can be treated with HIFU (High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound), but the effectiveness of the treatment may vary depending on the size, location, and type of the lesion.
In some cases, surgical removal may be more appropriate, so it is important to first accurately diagnose the condition of the uterus to determine whether HIFU is a suitable option.
| HIFU Treatment | Myomectomy | Hysterectomy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Principle | Necrotizes only the fibroid using high-intensity ultrasound without anesthesia or incision — no pain or bleeding | Makes three small incisions in the belly button and lower abdomen to insert surgical instruments and remove only the fibroid | Makes a 7 cm incision in the lower abdomen to surgically remove the entire uterus |
| Hospitalization | Resume daily life the day after the procedure | 4 – 5 days | 5 – 7 days |
| Warnings | Possibility of mild burns or minor blistering | Risk of damage to surrounding organs or adhesions | Pregnancy is no longer possible, with potential physical and psychological aftereffects |

Frequently Asked Questions
What are uterine fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are benign tumors that develop in the smooth muscles of the uterus. They are particularly common in women in their 30s and 40s. The exact cause is not fully understood, but factors such as female hormones (estrogen) and genetics may play a role.
What symptoms can uterine fibroids cause?
Approximately 10-20% of uterine fibroids cause symptoms, which can include increased pelvic pain, pressure on surrounding organs, infertility or miscarriage risks, and increased menstrual bleeding. The severity of symptoms often depends on the size, number, and location of the fibroids.
What are the different types of uterine fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are categorized based on their location within the uterus:
- Intramuscular fibroids: Develop within the uterine muscle layer, potentially altering the uterus’s shape and causing severe menstrual pain and increased menstrual blood flow.
- Submucosal fibroids: Occur in the endometrium and can lead to significant bleeding and complications, often being a direct cause of infertility.
- Subserosal fibroids: Develop within the membrane surrounding the uterus and typically cause no noticeable symptoms.
Is removal of uterine fibroids always necessary?
Not all uterine fibroids require removal. Treatment decisions depend on factors such as the size, location, and symptoms of the fibroids. If they interfere with daily life or grow larger, treatment may be essential. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
What treatment options are available for uterine fibroids?
Treatment options for uterine fibroids vary based on individual circumstances and may include:
- Medication: To manage symptoms such as pain and heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Non-invasive procedures: Such as High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) therapy, which uses focused ultrasound waves to target and treat fibroids without incisions.
- Minimally invasive procedures: Including uterine artery embolization, which blocks blood flow to the fibroids, causing them to shrink.
- Surgical options: Such as myomectomy (removal of fibroids while preserving the uterus) or hysterectomy (removal of the uterus), depending on the severity and patient preferences.
