Stem Cell Treatment in Korea
What are Stem Cells?
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can differentiate into about 210 types of tissue cells that make up the body. Because of their ability to self-replicate and differentiate into various types of cells, they have opened the way to treating intractable and chronic diseases that were previously difficult to treat.
In particular, embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells have the property of being able to differentiate into all types of cells, hence the name “pluripotent.”
Stem cells have recently begun to attract attention in the field of regenerative medicine because they play an important role in tissue regeneration and repair of damaged organs.
For example, research is being conducted to treat various diseases such as heart disease, brain disease, spinal cord injury, and diabetes using stem cells. Research is also actively being conducted on artificial tissues that replace damaged tissues or organs. For example, methods for transplanting artificial skin or cartilage are currently being developed.

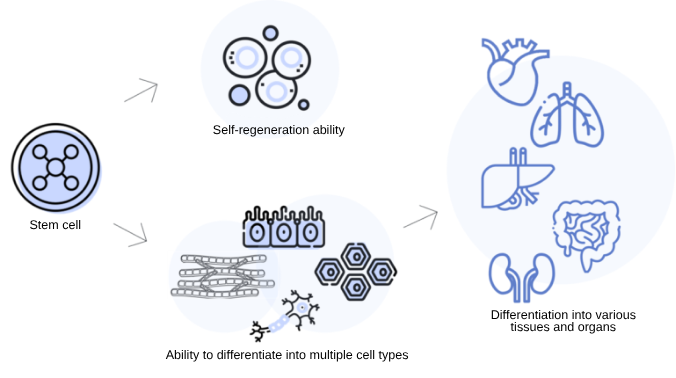
Stem cell differentiation
Stem cell differentiation is the process when stem cells transform into specific tissue cells, and the type of cell a stem cell will transform into is determined by various internal and external signals.
Internal signals are processes that regulate gene expression, while external signals are stimuli from other cells or growth factors. As stem cell differentiation progresses, the cells gradually transform into mature cells with specific functions.
For example, stem cells that differentiate into nerve cells acquire the function of neural transmission in the brain.
Types of Stem Cells
Stem cells are largely divided into embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells. Embryonic stem cells can differentiate into all tissues of the human body and are called pluripotent cells, but use of them is prohibited in principle due to ethical issues. On the other hand, adult stem cells are collected from already grown body tissues and can differentiate according to the characteristics of each organ.
Embryonic stem cells
Embryonic stem cells are cells derived from fertilized eggs that have the ability to differentiate into almost any type of cell in the human body. (For example, embryonic stem cells can differentiate into heart cells, nerve cells, skin cells, etc.)
These characteristics make it possible to use embryonic stem cells to differentiate into desired tissues and regenerate damaged tissues, but research is difficult due to ethical issues surrounding the destruction of embryos in the process of extracting cells from them.
adult stem cells
Adult stem cells are cells that have already been differentiated to perform specific functions and can be easily and safely collected from fat, bone marrow, placenta, and umbilical cord.
Because they can only differentiate into specific tissues or cells, their abilities are limited compared to embryonic stem cells. For example, stem cells derived from bone marrow differentiate into blood cells, and stem cells derived from muscle differentiate into muscle cells. However, adult stem cells can be obtained without destroying the embryo, so there is no ethical controversy.
Revolutionary healing powered by a single stem cell
Stem Cell Therapy – Target Issues and Effects
The main effects of stem cells, which play a vital role in tissue regeneration and repairing damaged cells, are as follows:

Cartilage regeneration and treatment of joint and musculoskeletal diseases 
Anti-aging with wrinkle improvement, skin regeneration and elasticity enhancement 
Strengthens hair roots and improves hair loss 
Improvement of immune diseases such as atopy and rheumatism 
Treatment of brain diseases such as dementia, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s disease 
Improving women’s vaginal health and men’s sexual function
Stem Cell Therapy – Orthopedics
In 2023, the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons proposed stem cell treatment as the standard of care for most arthritis, ligament damage, and muscle damage. Stem cells are the last treatment option before surgery, and SH Clinic can solve various orthopedic problems through accurate diagnosis.
① Stem cell treatment for knee arthritis has been designated as a new medical technology and is now covered by insurance. This stem cell treatment is a good way to alleviate arthritis before it gets to the point where it requires artificial joints.
② Stem cell treatment can be a good option for chronic tendonitis that does not heal well, such as frozen shoulder, tennis elbow, and plantar fasciitis.
③ It is also effective for spinal diseases such as chronic back pain, disc, and cervical pain that do not improve despite various treatments.
④ The American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons reported that using stem cells for quicker recovery after surgery increases the effectiveness of the surgery and shortens the recovery period. Therefore, stem cell treatment after surgery can also show good results for patients.
Procedure Process Explanation
Frequently Asked Questions
What is stem cell therapy?
Stem cell therapy involves using undifferentiated cells that can transform into various tissue types to repair or replace damaged tissues and organs. These cells have the unique ability to self-replicate and differentiate into about 210 types of tissue cells that make up the body, making them valuable in treating chronic and intractable diseases.
What types of stem cells are used in treatments?
Stem cells are primarily categorized into embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells. Embryonic stem cells can differentiate into all tissue types but are generally not used due to ethical concerns. Adult stem cells are harvested from grown body tissues and can differentiate according to the characteristics of each organ, making them suitable for various therapeutic applications.
What conditions can be treated with stem cell therapy?
Stem cell therapy is being researched and applied in treating a variety of conditions, including heart disease, brain disease, spinal cord injuries, diabetes, and degenerative diseases. It is also used in regenerative medicine to repair damaged tissues or organs, such as artificial skin or cartilage transplants.
How does stem cell differentiation work?
Stem cell differentiation is the process by which stem cells transform into specific tissue cells. This transformation is guided by various internal signals, such as gene expression regulation, and external signals, including stimuli from other cells or growth factors. As differentiation progresses, stem cells gradually acquire the functions of mature cells in specific tissues.
What are the ethical considerations in using embryonic stem cells?
The use of embryonic stem cells involves ethical concerns because they are derived from fertilized eggs and have the potential to develop into any cell type in the human body. Due to these ethical issues, the use of embryonic stem cells is generally prohibited or highly regulated, leading to a focus on adult stem cells in therapeutic applications.