Neuroplasty in Korea
Treat a slipped disc with injections, not surgery.
Procedure Process Explanation
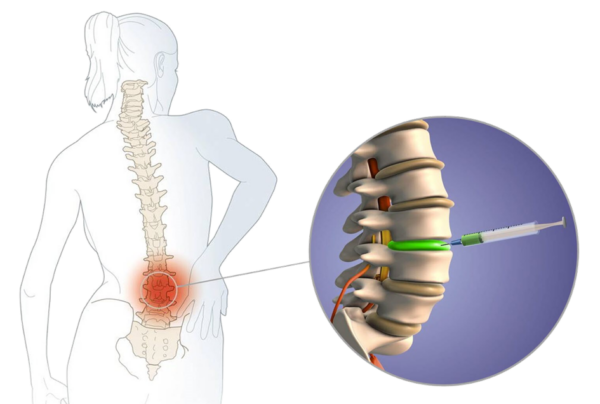
What is neuroplasty?
Neuroplasty is a non-surgical treatment used to address herniated discs in the lower back or neck, as well as spinal stenosis. A microcatheter, only 1mm in diameter, is inserted through a small opening between the vertebrae to deliver special medication directly to the affected area.
Its greatest advantages are minimal scarring, low risk of side effects, and high safety—making repeated treatments possible.
Cervical (neck) neuroplasty, in particular, is a highly advanced procedure performed by only a few hospitals in Korea. It is considered a safe treatment option even for patients who may have difficulty undergoing surgery due to conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, or heart disease.
Neuroplasty procedure Information
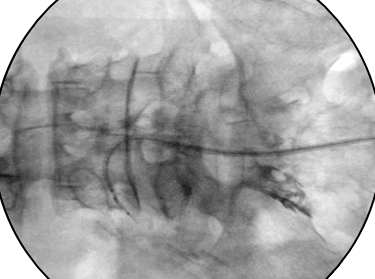
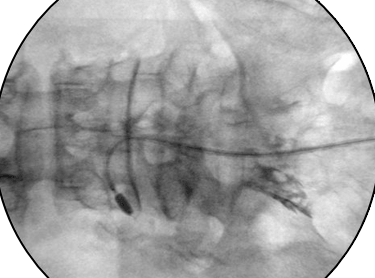
Neuroplasty addresses the issue where medication cannot effectively reach the affected area due to adhesions between the herniated disc and surrounding nerves, often caused by inflammation. In this procedure, a thin catheter (about 1–2 mm in diameter) is inserted through the tailbone, and the treatment area is monitored in real-time using a C-arm imaging device. Medication is then administered precisely to break down adhesions and reduce inflammation.
Approximately 90% of patients with herniated discs can expect improvement through this procedure.
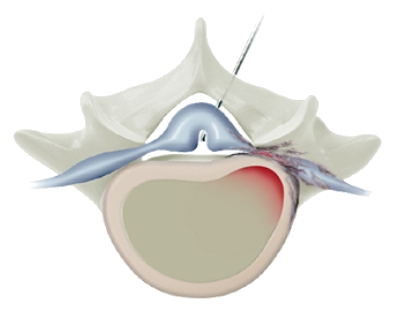
STEP 1
A 1mm diameter micro catheter is inserted between the vertebrae.
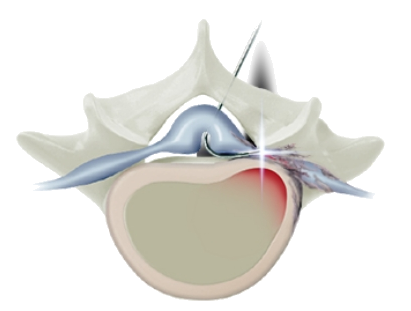
STEP 2
A specially designed needle is inserted and guided to approach the source of the pain.
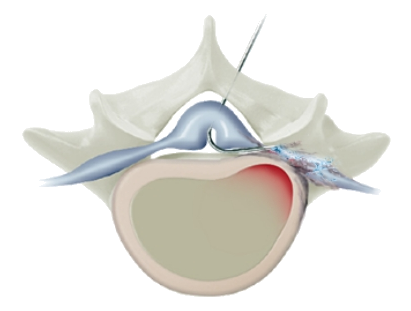
STEP 3
Removal of inflammation or adhesions around the lesion.
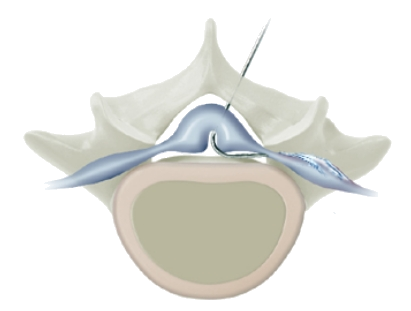
STEP 4
Treatment by injecting special drugs into the lesion.
Advantages of Neuroplasty
Candidates for Neuroplasty
Precautions After Neuroplasty
Widening the narrowed spinal canal with neurolysis
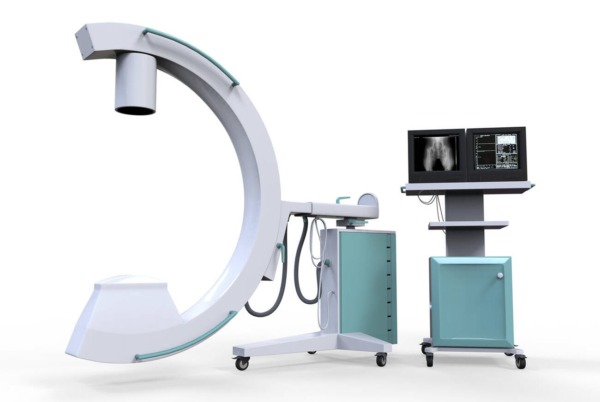
X-ray imaging device C-Arm
A C-Arm is a mobile X-ray imaging device commonly used in operating rooms and emergency rooms to provide precise diagnostic imaging. By transmitting X-rays through the treatment area, it delivers real-time visual information about the condition of bones and nerves, as well as the presence, size, and location of lesions. It is an essential tool for image-guided procedures, ensuring accuracy and safety during surgery.
Using the high-resolution digital imaging medical device C-Arm enables accurate diagnosis and leads to prompt and precise procedures.
Photo of Neuroplasty captured with C-Arm imaging