Adenomyosis in Korea
Ultrasound treatment relieving endometrial tissue growth
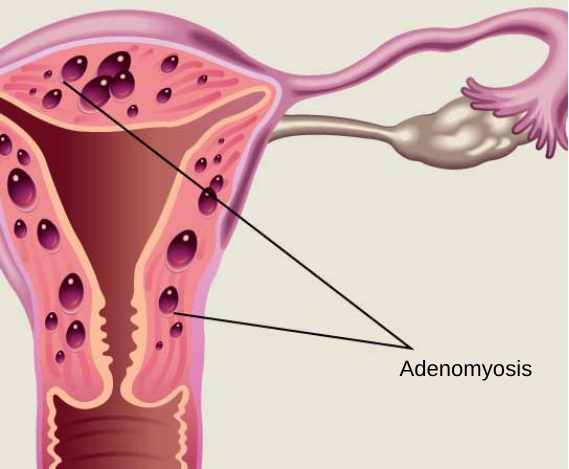
What is Adenomyosis?
Adenomyosis is the term for when the endometrial tissue, the innermost layer of the uterus, grows into the uterine muscle layer.
Endometrial tissue has the characteristic of growing and breaking down according to the menstrual cycle, and the endometrial tissue that has invaded the uterine muscle layer follows this same cycle despite being displaced.
Adenomyosis can cause the uterus to double or triple in size, and presents symptoms such as heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, severe cramps, chronic pelvic pain, and pain during sexual intercourse.
Causes of Adenomyosis
The cause of adenomyosis has not been clearly identified, but in most cases it is known to be caused by genetic factors or an imbalance in hormonal secretions.
Symptoms of Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis can cause heavier bleeding than normal menstruation and lead to intense menstrual cramps by increasing uterine muscle contractions, secretion of inflammatory substances, and overstimulation of nerves. In severe cases, this may result in lowered fertility or even infertility.
Heavy menstrual bleeding and severe menstrual cramps
Severe menstrual cramps may be accompanied by heavy menstrual bleeding, which can lead to anemia.
enlarged uterus
An enlarged uterus may cause pain and lead to abnormal bleeding outside of the menstrual cycle.
Infertility due to intrauterine bleeding
Bleeding inside the uterus can interfere with implantation of a fertilized egg, causing infertility.
Uterine contractions
Uterine contractions can interfere with a stable pregnancy, increasing the risk of early miscarriage.
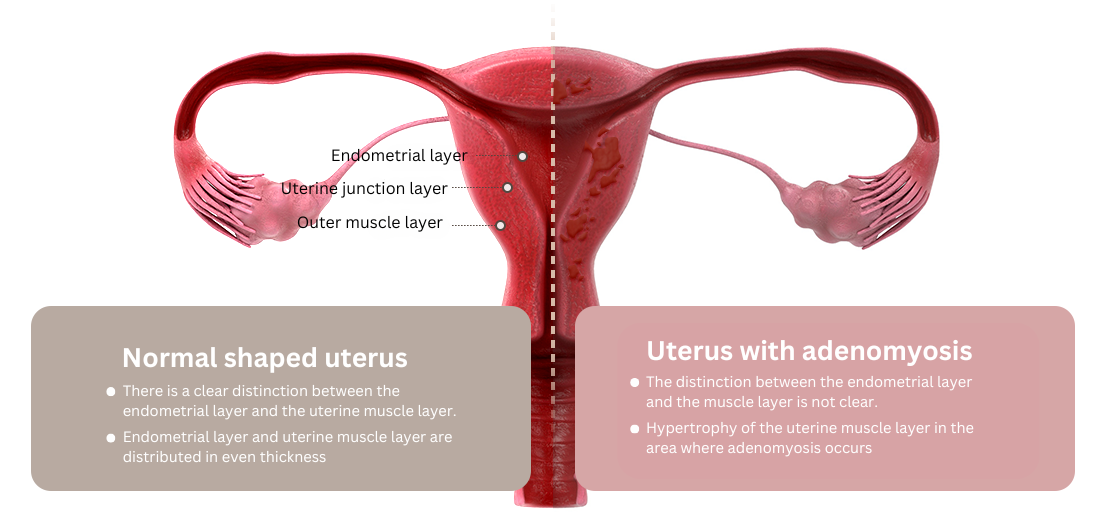
Difference between adenomyosis and uterine fibroids
Adenomyosis and uterine fibroids are similar but distinct conditions. While uterine fibroids are a separate mass, adenomyosis is a condition in which the endometrium abnormally invades the uterine tissue, causing the uterus to thicken.
Unlike fibroids, adenomyosis has unclear boundaries and the affected areas are scattered, making it more challenging to treat.
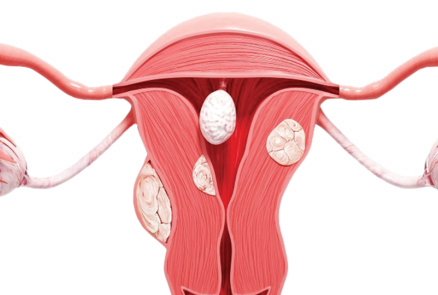
▪️ A tumor formed by uterine muscle tissue
▪️ Symptoms vary depending on the size and location of the fibroid.
▪️ The boundaries between the lesion and surrounding muscle tissue are clearly defined, making detection and removal relatively easier
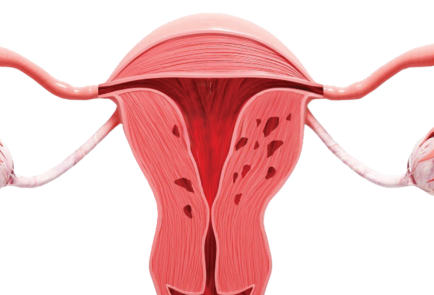
▪️ Abnormal proliferation of endometrial tissue in the muscle layer
▪️ If you have adenomyosis, you are more likely to show symptoms
▪️ The boundary between the lesion and normal tissue is unclear, making treatment and removal more difficult
HIFU Treatment Can Help Alleviate Adenomyosis Symptoms
Treatment of uterine fibroids and adenomyosis
Most cases of uterine fibroids and adenomyosis can be treated with HIFU (High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound), but the effectiveness of the treatment may vary depending on the size, location, and type of the lesion.
In some cases, surgical removal may be more appropriate, so it is important to first accurately diagnose the condition of the uterus to determine whether HIFU is a suitable option.
| HIFU Treatment | Myomectomy | Hysterectomy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Principle | Necrotizes only the fibroid using high-intensity ultrasound without anesthesia or incision — no pain or bleeding | Makes three small incisions in the belly button and lower abdomen to insert surgical instruments and remove only the fibroid | Makes a 7 cm incision in the lower abdomen to surgically remove the entire uterus |
| Hospitalization | Resume daily life the day after the procedure | 4 – 5 days | 5 – 7 days |
| Warnings | Possibility of mild burns or minor blistering | Risk of damage to surrounding organs or adhesions | Pregnancy is no longer possible, with potential physical and psychological aftereffects |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is adenomyosis?
Adenomyosis is a condition where the endometrial tissue, which normally lines the uterus, grows into the muscular wall of the uterus. This can cause the uterus to enlarge and lead to symptoms such as heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, severe cramps, chronic pelvic pain, and pain during sexual intercourse.
What causes adenomyosis?
The exact cause of adenomyosis is not clearly identified, but it is commonly believed to be related to genetic factors or hormonal imbalances.
What are the symptoms of adenomyosis?
Symptoms of adenomyosis include heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, severe menstrual cramps, chronic pelvic pain, pain during sexual intercourse, and an enlarged uterus. In severe cases, it may lead to infertility or increased risk of miscarriage.
How is adenomyosis diagnosed?
Adenomyosis is diagnosed through a detailed examination conducted by a specialist, which may include a personal consultation, pelvic examination, and imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI to assess the severity and type of adenomyosis.
What treatment options are available for adenomyosis at SH Clinic in Korea?
SH Clinic in Korea offers a variety of treatment options for adenomyosis, including personalized treatment plans decided through a 1:1 consultation with a specialist. Treatments may involve hormone regulation therapy, high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU), or high-frequency dissolution, utilizing state-of-the-art medical equipment to ensure safe and effective treatments that aim to minimize side effects.
What is the recovery process like after adenomyosis treatment at SH Clinic?
The recovery process at SH Clinic varies from patient to patient, depending on individual conditions and the type of treatment received. The clinic provides continuous support through periodic follow-up checkups to ensure optimal recovery and management after the procedure, with customized treatment plans by experienced obstetricians/gynecologists to help patients recover at their own pace.
How is adenomyosis different from uterine fibroids?
Adenomyosis and uterine fibroids are similar but distinct conditions. Uterine fibroids are separate masses formed by uterine muscle tissue, whereas adenomyosis involves the endometrial tissue abnormally invading the uterine muscle layer, causing the uterus to thicken. Unlike fibroids, adenomyosis has unclear boundaries and the affected areas are scattered, making it more challenging to treat.
